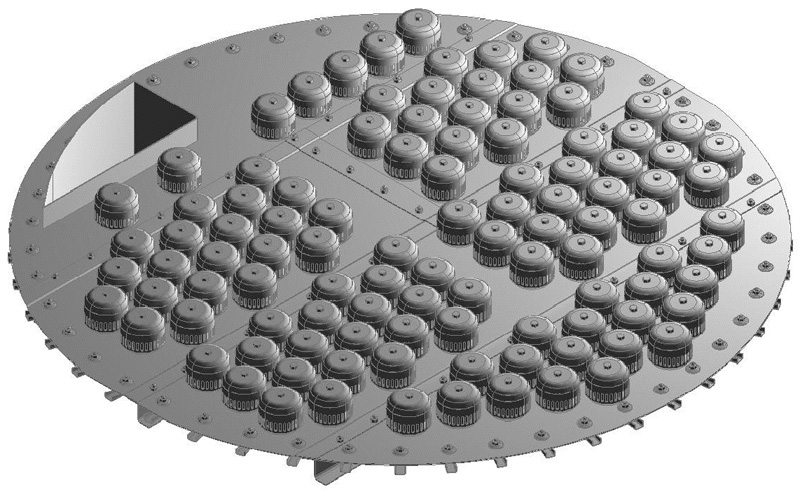
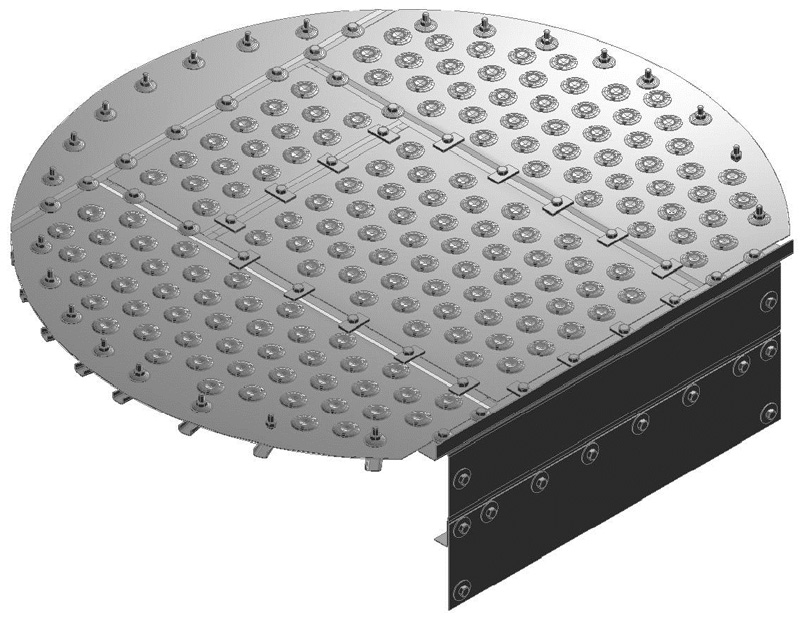
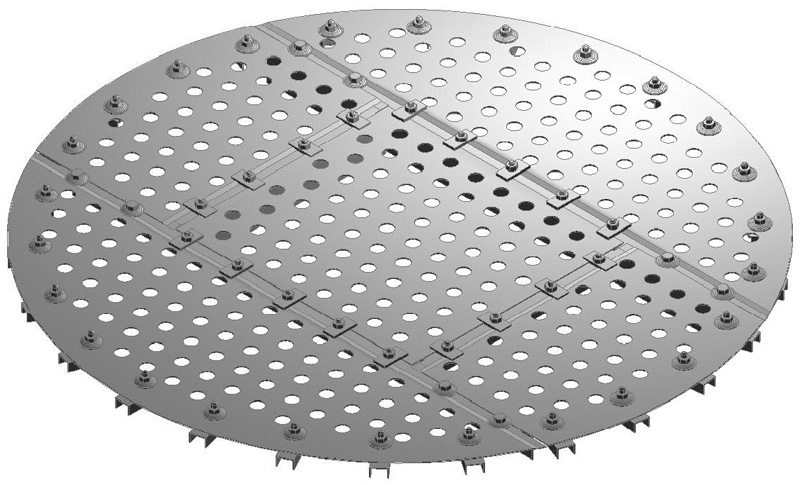
Conventional Trays
THE BEST PARTNER HANBIT SOLTECH
The three main tray types in the market today are the bubble cap tray, the sieve tray, and the valve tray. Each has relative advantages and disadvantages although the valve tray is by far the most widely used. We offer a complete line of conventional trays including dual-flow, baffle trays and related equipment.
※ If the entire table is not visible, you can scroll the table left and right to check the entire table..
| Type | Bubble-cap tray | Sieve tray | Valve tray | Dual-flow tray |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity | Moderate | High | High to very high | Very high |
| Efficiency | Moderate | High | High to very high | Lower than other types |
| Turndown | Excellent (10:1) | About 2:1 | 4:1, up to 6-7:1 | Low |
| Entrainment | High | Moderately high | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Pressure drop | High | Moderately high | Moderate | Low |
| Maintenance | Relatively high | Low | Low to moderate | Low |
| Fouling Tendency | High | Low | Moderate | Extremely low |
| Cost | High | Low | Low to moderate | Very low |
Bubble Cap Tray
Bubble cap tray is a flat perforated plate with risers around the holes, and caps in the form of inverted cups over the risers. The caps are usually equipped with slots through which the vapor comes out. Liquid and froth are trapped on the tray to a depth at least equal to the weir height or riser height, giving the Bubble cap tray a unique ability to operate at low vapor and liquid rates.
Due to their ability to operate at low vapor and liquid rates, bubble cap trays are used primarily when large turndown ratios are required. This tray is the most expensive option and it has lower capacity compared to sieve and valve trays. Bubble cap can be offered in 3”, 4”, 6” OD and custom sizes as well.
Main Applications
✔ Extremely low flow conditions✔ Where leakage must be minimized
Advantage
• Well known performance• Good liquid seal
• High turndown (10:1)
• High liquid residence time
Disadvantage
• High material cost• High installation cost
• Long installation period
• Low capacity than sieve tray
• Non-uniform flow due to high liquid gradient
Sieve Tray
Sieve tray is a flat perforated plate. Vapor issues from the holes to give a multi-orifice effect. The vapor velocity keeps the liquid from flowing down through the holes. At low vapor velocity, liquid weeps through the holes, bypassing some of the tray and reducing efficiency, giving sieve trays relatively poor turndown. Sieve trays are simple and easy to fabricate, and are therefore relatively inexpensive.
Sieve trays have been used widely in the petroleum and chemical industries for many years because they are the most economical trays when low turndown is required. When properly designed, they have a capacity and efficiency equivalent to other types of general purpose trays. They can also be used in moderately dirty services.
Main Applications
✔ Most columns when turndown is not criticalAdvantage
• High capacity than bubble cap tray• Low liquid gradient
• Fouling resistance (with large orifice hole)
• Relatively low cost
Disadvantage
• Low turndown ratio (2:1)• Prone to vibration at low rate
Floating Valve Tray
Floating valve tray has round movable valves with or without a caging structure on perforated plate. The valve disks rise as vapor rate is increased. The upper limit of opening is controlled by a caging structure or by restrictive legs at the bottom of the valve unit. As vapor rate falls, the disk openings are reduced, or they may settle intermittently over the holes. This stops the liquid from weeping and gives the valve tray its main advantage; good operation at low flow rates, and therefore, a high turndown.
Floating valve tray exhibits lower entrainment than sieve tray because the flow of vapor through the holes is horizontal by valve unit. They have an efficient operating range (turnodwn) superior to a sieve tray when both are designed for the same maximum capacity. They are a much simpler, lower pressure drop and lower cost alternate to the bubble cap tray. The only drawback to using the floating valve tray is that valves can plug and they are difficult to clean when plugged.
Main Applications
✔ Most columns✔ Services where turndown is important
Advantage
• More capacity than sieve or bubble cap tray• Good turndown (4:1, up to 6-7:1)
• Good efficiency
• Same cost as sieve tray
Disadvantage
• Can plug• Difficult to clean when plugged
Dual Flow Tray
Dual flow tray is a sieve tray with no downcomers. Tray Holes have a dual function to pass both liquid and vapor. This tray operates with liquid continuously weeping through the holes, hence its low efficiency. Tray froth height diminishes rapidly when vapor velocity is reduced, causing further efficiency deterioration upon turndown. Turndown of a dual flow tray is even poorer than that of a sieve tray with downcomers. Dual flow trays are prone to channeling, and are therefore sensitive to out of levelness and to liquid distribution.
As such, the use of dual flow trays may be more advantageous than other contacting devices, especially dual flow trays are now primarily utilized for fractionation of polymerizable compounds because of their low hold-up and ease of cleaning.
Main Applications
✔ Capacity revamps where efficiency and turndown can be sacrificed✔ Highly fouling and corrosive services
Advantage
• Greater capacity than common valve tray• Fouling resistance
• Low pressure drop
• Relatively low cost
Disadvantage
• Relatively low efficiency• Low turndown ratio (smaller than sieve tray)
• Sensitive to leveling
Baffle Tray
Baffle trays are arranged in a tower in such a manner that the liquid flows down the column by splashing from one baffle to the next lower baffle and the ascending gas or vapor passes through the “curtains” of liquid spray descending from baffle to baffle.
Baffle trays are generally designed to give a maximum dispersion of liquid and an optimum contact of liquid and vapor with high capacities. They are well suited for heat transfer applications including heavy oil refining with high solids.
Main Applications
✔ Heavy oil refining and petrochemical industries in heat transfer applicationsAdvantage
• Very high capacity• Fouling resistance
• Very low pressure drop
• Relatively low cost
Disadvantage
• Poor efficiency (due to the low contact area)